Theme 1: Neural Circuit in the Visual and Visual Association Areas.
We evaluated the visual cortical circuit through the occipito-parietal
and occipito-temporal pathways using several tracers in macaque monkeys
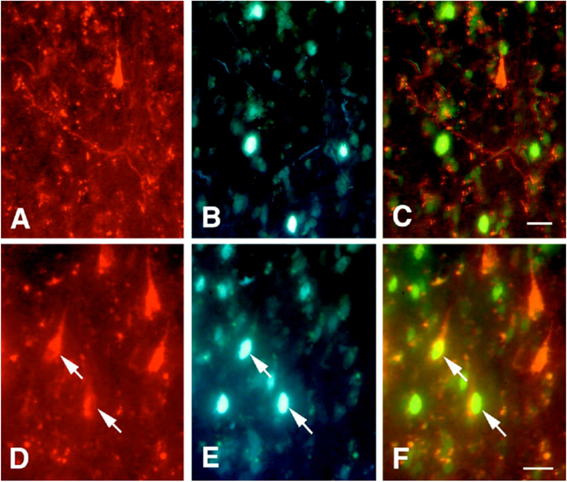
(Macaca mulatta and Macaca fuscata). Figure 1 shows retrogradely labeled neuronal cell bodies and orthogradely
labeled fibers and terminals in the lateral intraparietal area LIP after
the injections of rhodamine (red) into the visual area V3A and of fast
blue (blue) into the anterior intraparietal area AIP. The red arrows in
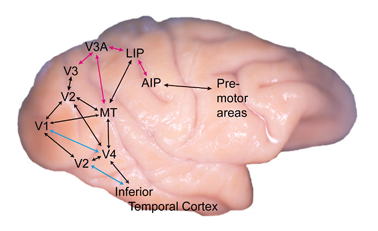
Figure 2 show the results. This circuit processes the information of three-dimensional
visual objects that is necessary for hand shaping of object manipulation.
The blue arrows in Figure 2 show bypath routes in the occipito-temporal
pathways that we found during my stay in NIH.
Figure 3.
Theme 3: Visually Evoked Emotion and its Regulation.
An fMRI project is in progress to evaluate the relationship between emotion and vision.
Hiroyuki Nakamura, M.D., Ph.D.
Theme 2: Crossroad between Emotion and Sense.
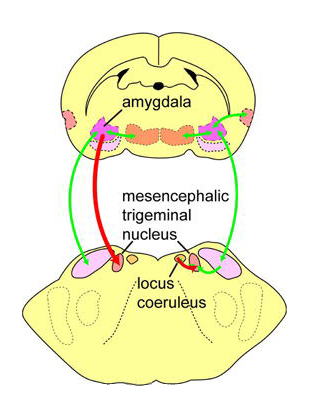
The red arrows in Figure 3 show direct projections from the central amygdala
nucleus, the output center of emotion, and from the locus coeruleus, noradrenergic
nucleus that relates to fight, to the mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus.
The nucleus conveys proprioceptive sensory signals from the masticatory
muscles and periodontal regament. The results thus suggest that sensory
inputs are directly regulated by emotion centers.
Figure 1.
Figure 2.